The difference between DFR1 and DFR valves is that DFR1 has a small, blocked orifice in the middle. What is the function of this orifice?
 Posted on 13/12/2025
Posted on 13/12/2025
In A10VSO, what are the differences between the two control methods, DFR and DFR1?
1. Structural Differences
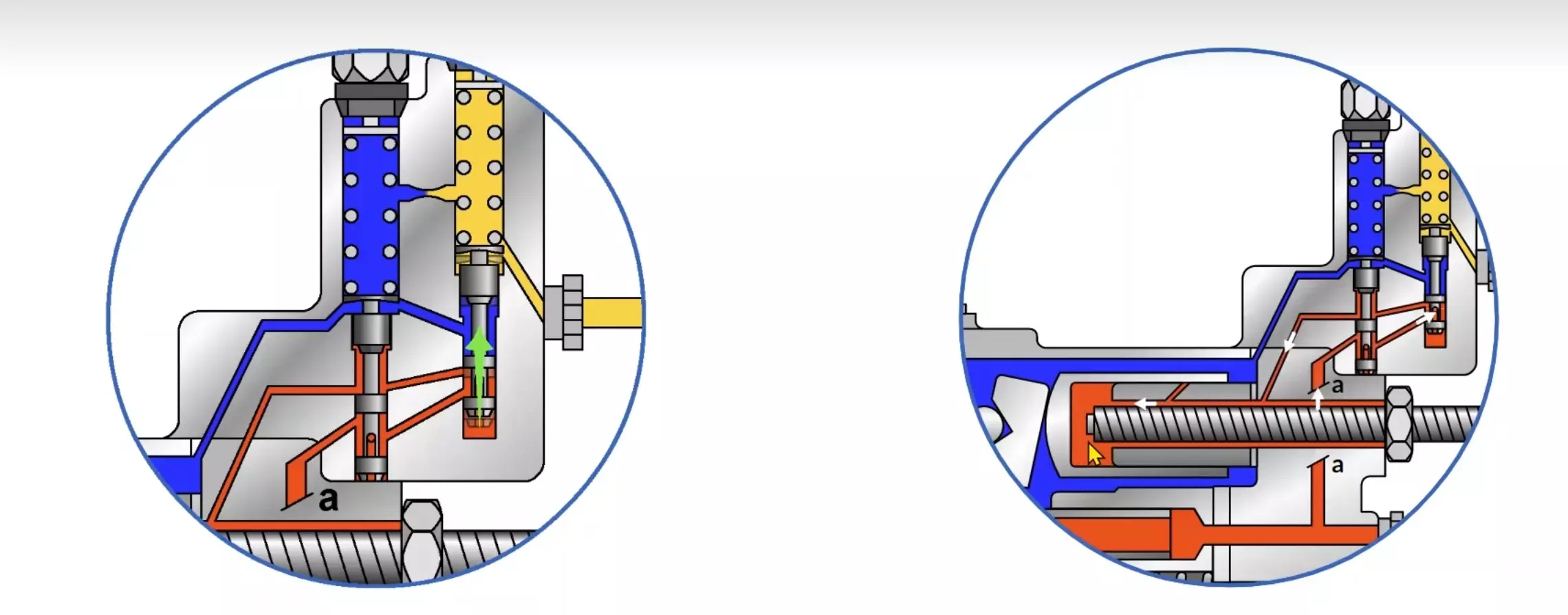
From Bosch Rexroth's sample code, we can see that DFR1 blocks the X-T channel compared to DFR, while the X-T channel in DFR is not blocked!
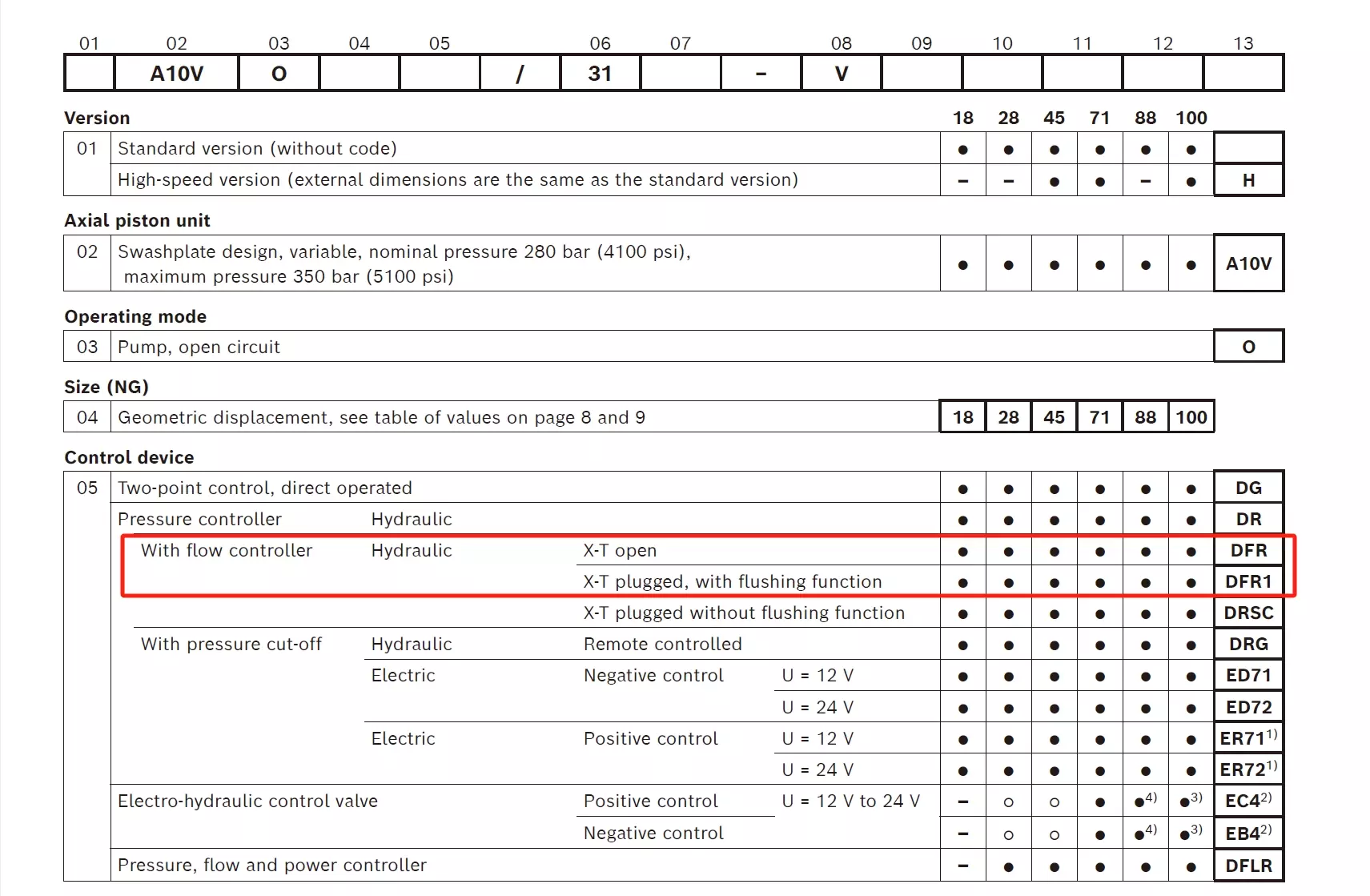
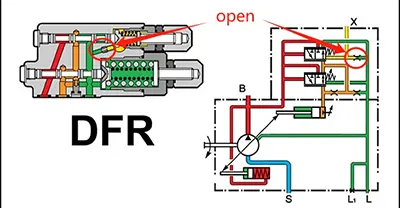
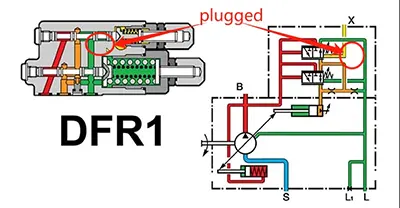
What is the X channel? It refers to the feedback port X. However, DFR1 doesn't actually block this feedback port. If this port were blocked, the pump's output pressure and flow rate couldn't be adjusted.
As shown in the diagram, DFR1 actually blocks a damping orifice on the right side of the FR flow control valve. Blocking this orifice disconnects the spring chamber on the right side of the FR flow control valve from the oil tank.
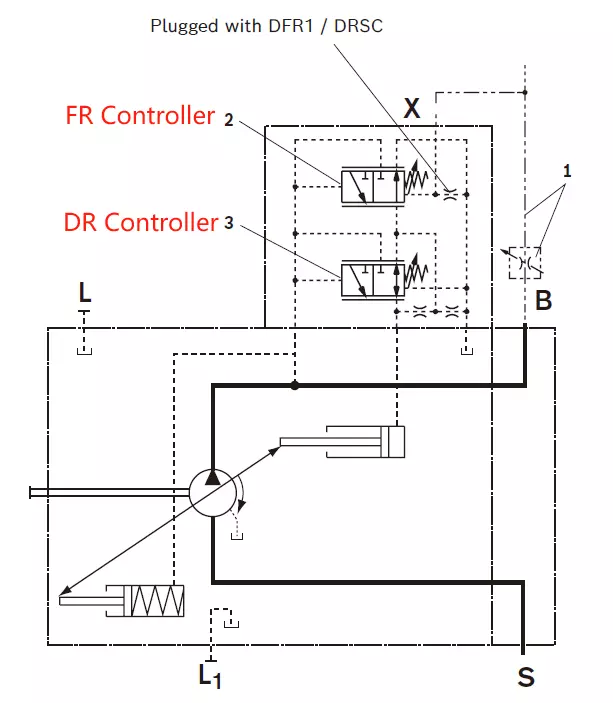
The DFR1 versions have no unloading between X and the reservoir. The LS must thus be unloaded in the system. Because of the flushing function of the flow controller in the DFR1 control valve, sufficient unloading of the X line must also be provided. If this unloading of the X line cannot be ensured, the DFR control valve must be used.
2. Functional Differences
To understand the functional differences between the two, let's first look at the role of the damping between the spring chamber and the discharge port of the FR flow control valve in a DFR pump.
The Role of this "Small Throttling Orifice" in a DFR Valve
In a DFR valve, this throttling orifice is typically located in the feedback oil circuit of the control piston (or valve core). Its main functions are:
Providing Damping
This throttling orifice and the control chamber volume form an RC damping circuit (R = throttling resistance, C = chamber volume);
When the system pressure or load-sensitive (LS) pressure changes abruptly, the flow of oil through this small orifice is obstructed, slowing down the movement of the control piston;
This prevents sudden changes in pump displacement, avoiding system pressure shocks (pressure overshoot) or flow oscillations.
Stabilizing the Control Process
Under steady-state conditions, this orifice helps maintain stable control chamber pressure;
This reduces high-frequency valve core vibration caused by rapid changes in external load (such as sudden cylinder stoppage), improving system stability.
Why does DFR1 need to "block" this throttle orifice?
Blocking the throttle orifice (i.e., eliminating damping) significantly improves the response speed of the control oil circuit, resulting in the following changes:
Advantages:
Faster dynamic response: The control piston can more quickly follow changes in load pressure (LS signal) and system pressure;
More timely flow regulation: Particularly suitable for operating conditions with frequent load changes (such as excavators, injection molding machines, etc.), it can more accurately maintain constant power;
Improved operating feel: In construction machinery, it can reduce "lag" and improve maneuverability.
Potential risks:
More prone to system oscillation or overshoot: Without other compensation measures, rapid response may lead to pressure fluctuations;
Higher requirements for oil cleanliness: Without throttle damping, the valve core is more sensitive, and contaminants are more likely to cause jamming or malfunction.
